recursion
"함수 호출 반복"
// recursion 예제
#include <stdio.h>
void up_and_down(int); // prototype
int main(void)
{
up_and_down(1); // 함수 호출 반복
return 0;
}
void up_and_down(int n)
{
printf("Level %d: n location %p\n", n, &n); // 1
if (n < 4)
up_and_down(n+1);
printf("LEVEL %d: n location %p\n", n, &n); // 2
}Level 1: n location 010FFA4C
Level 2: n location 010FF974
Level 3: n location 010FF89C
Level 4: n location 010FF7C4
LEVEL 4: n location 010FF7C4
LEVEL 3: n location 010FF89C
LEVEL 2: n location 010FF974
LEVEL 1: n location 010FFA4C
메모리적으로 접근해보면
level 4와 LEVEL 4는 같은 함수에서 실행된 것이므로
메모리 영역이 같다
UD(1)
{
l1
UD(2) // UD(2)가 L1코드보다 먼저 실행된다
L1
}
UD(2)
{
l2
UD(3) // 위와 동일
L2
}
UD(3)
{
l3
UD(4) // 위와 동일
L3
}
UD(4)
{
l4
// 같은 함수에서 실행되었기 때문에 변수 n의 저장 위치가 같음
L4
}
recursive VS iterative(loop-based)
"함수 호출 반복" VS "반복문 사용"
메모리 소모 많음 VS 적음
코드 간단 VS 어려움
// 예제 [factorial 계산]
long fact(int n) // loop-based function
{
long ans;
for (ans = 1; n > 1; n--)
ans *= n;
return ans;
}
long rfact(int n) // recursive version
{
long ans;
if (n > 0)
ans= n * rfact(n-1);
else
ans = 1;
return ans;
}순환 작동 순서 및 메모리 구조
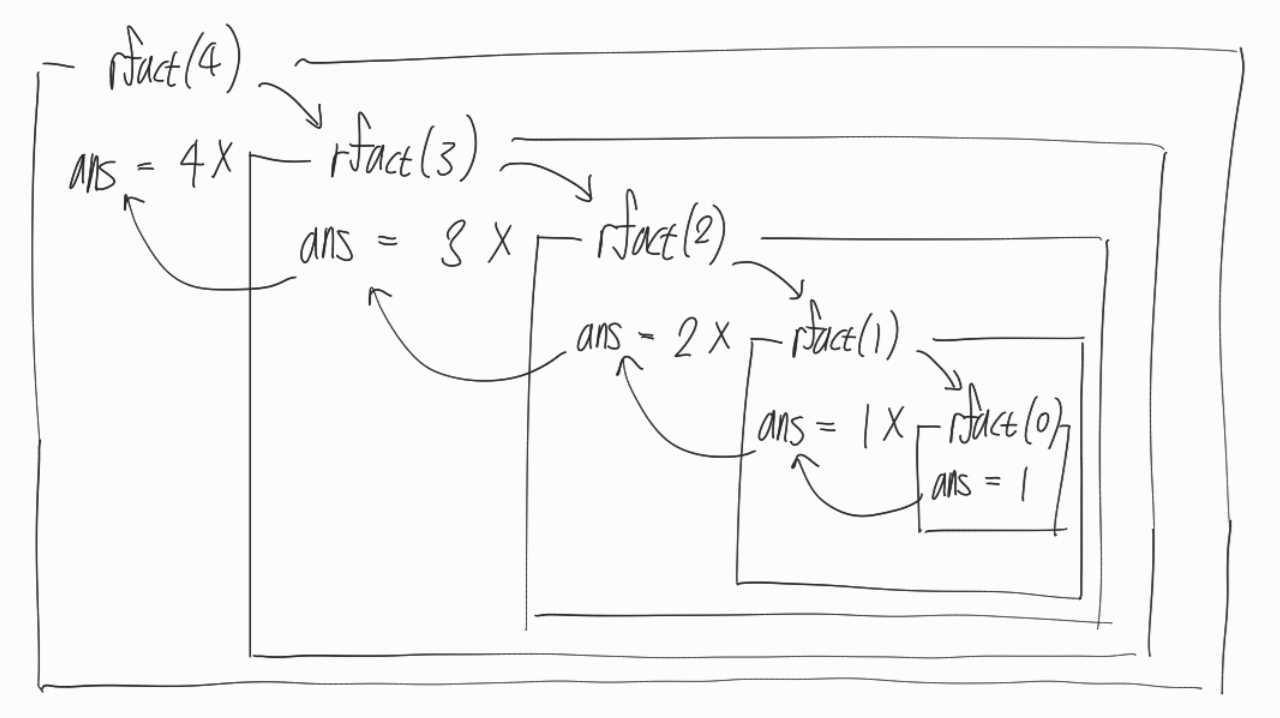
지역변수 ans는 각 함수마다 다르기 때문에 메모리 저장 위치도 다름
// 예제 [10진수 -> 2진수 출력]
#include <stdio.h>
void to_binary(unsigned long n);
int main(void)
{
unsigned long number;
printf("Enter an integer (q to quit):\n");
while (scanf("%lu", &number) == 1)
{
printf("Binary equivalent: ");
to_binary(number);
putchar('\n');
printf("Enter an integer (q to quit):\n");
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
void to_binary(unsigned long n) /* recursive function */
{
int r;
r = n % 2;
if (n >= 2)
to_binary(n / 2);
putchar(r == 0 ? '0' : '1');
// putchar('0' + r); ASCII code 적용
return;
}순환 작동 순서
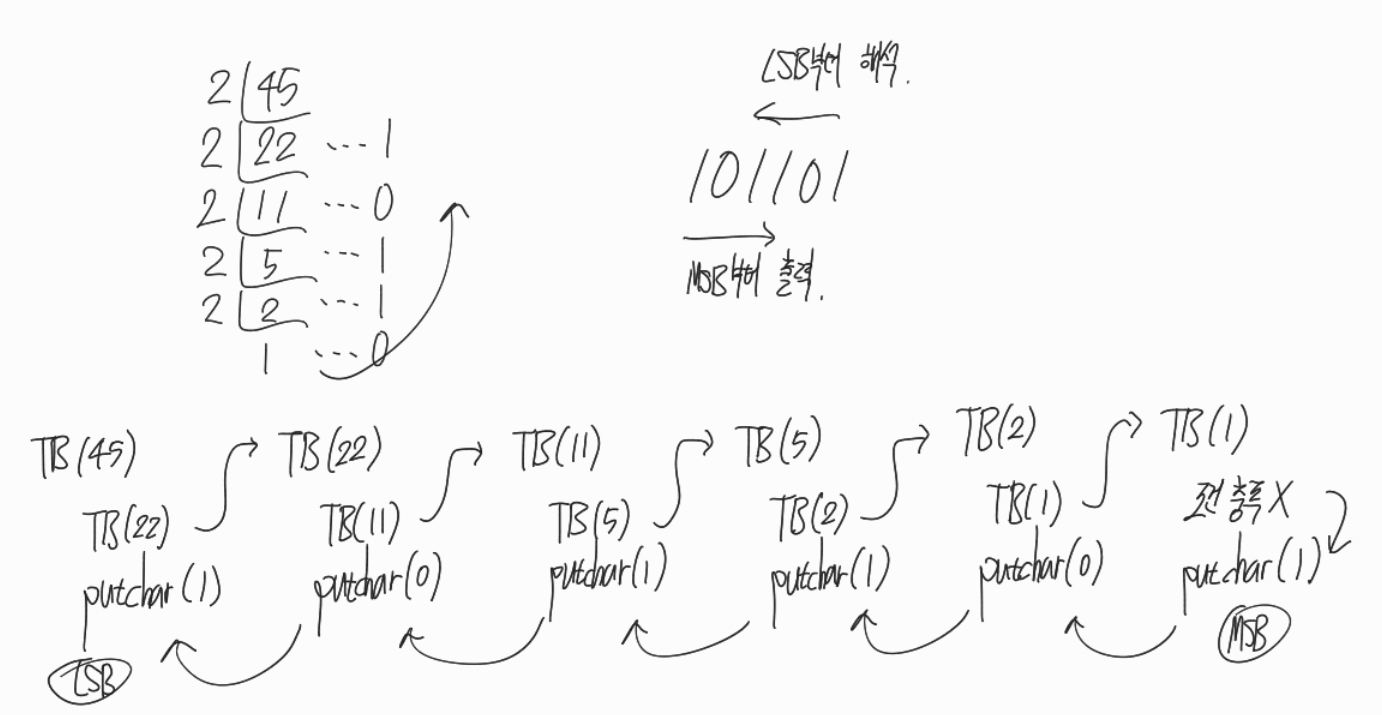
순환이 시작되는 시점을 기준으로
위쪽 코드와
밑 코드의 작동순서를 기억하자
// 예제 [하노이 탑]
#include <stdio.h>
void hanoi_tower(int n, char from, char tmp, char to)
{
if( n==1 ) printf("원판 I을 %c에서 %c으로 옮긴다.\n", from, to);
else {
hanoi_tower(n-1, from, to, tmp);
printf("원판 %d을 %c에서 %c으로 옮긴다.\n", n, from, to);
hanoi_tower(n-1, from, to, tmp);
}
}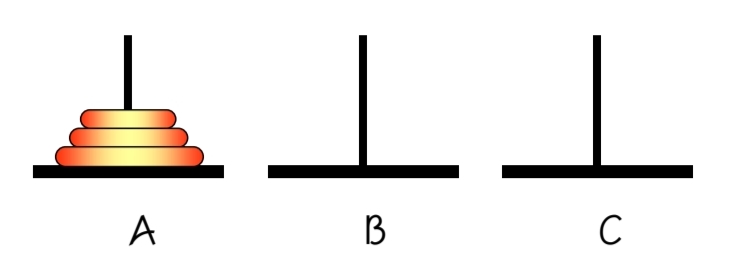
A 에서 B로 원판을 이동시키는 코드
이경우에는 순서가 더 복잡하다
'CS > Data Structure & Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [String] 1. 문자 찾기 (0) | 2022.08.04 |
|---|---|
| List (0) | 2021.12.02 |
| deque (0) | 2021.12.02 |
| Queue (0) | 2021.11.25 |
| Stack (0) | 2021.11.23 |
